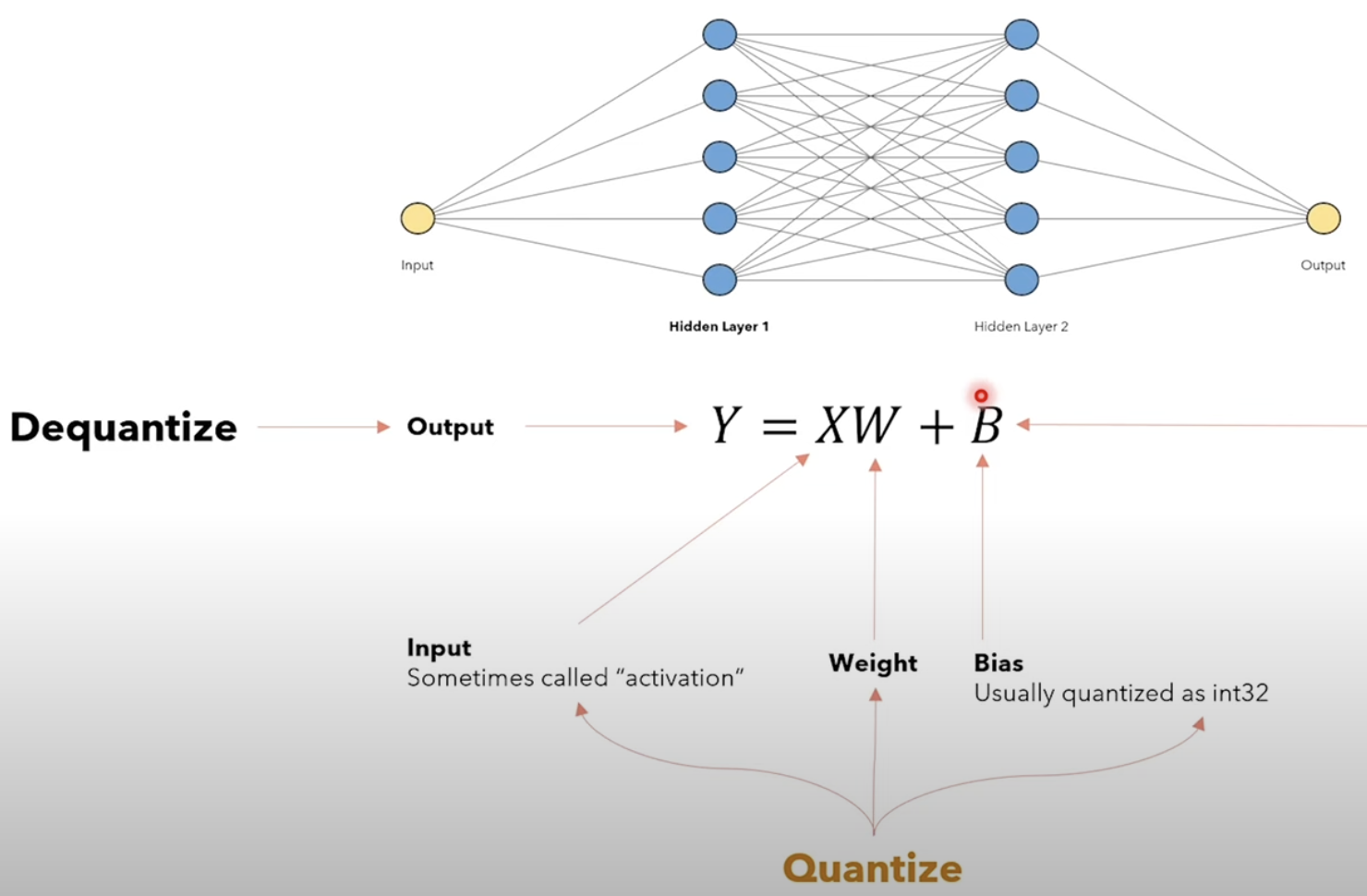
Quantization¶
Aims to reduce the precision of the model weights and activations. Usually by changing the data type from floating point to integer.
Benefits:
- Reduced memory usage
- Faster inference
- Reduced model size
Types:
- Symmetric: same quantization for positive and negative values
- Asymmetric: different quantization for positive and negative values
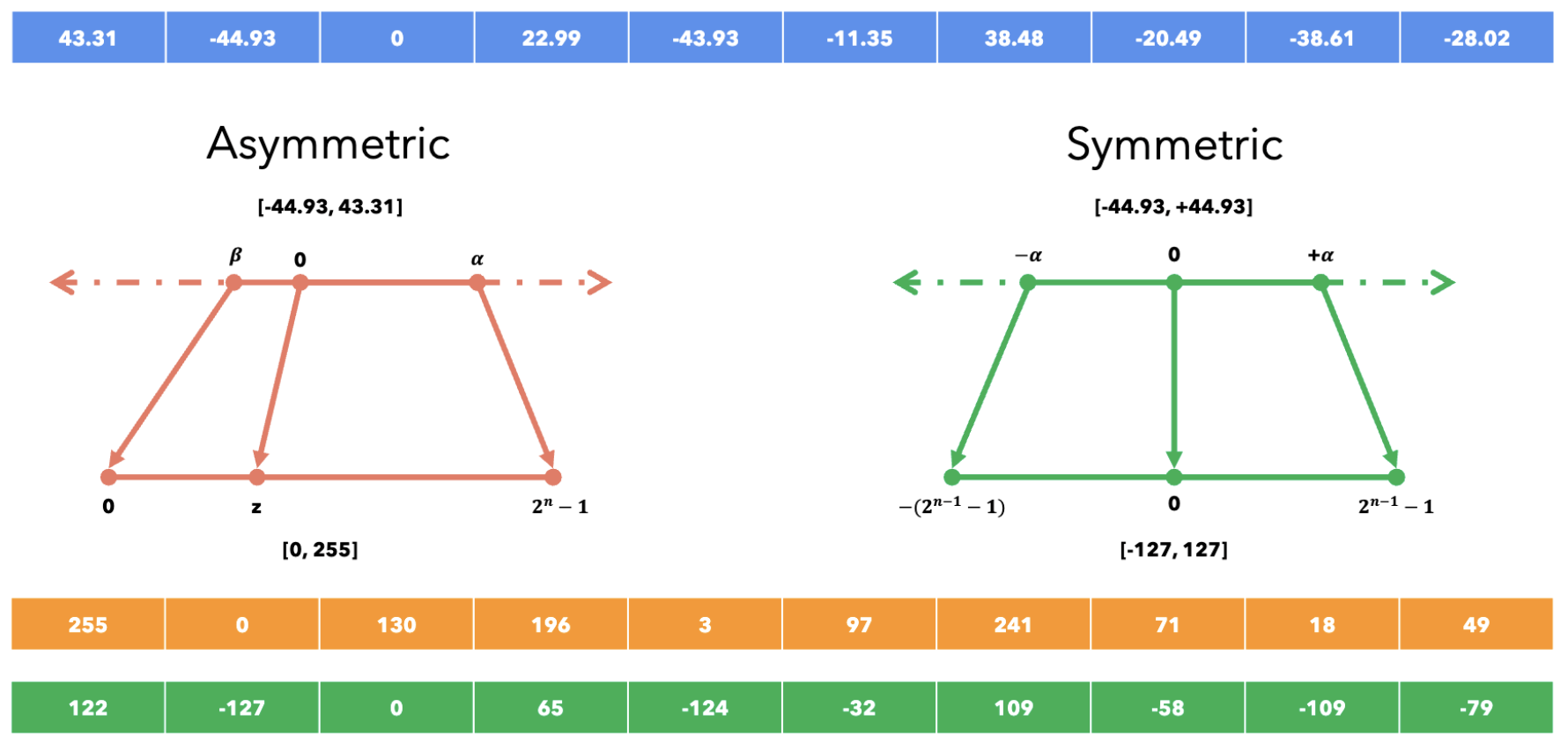
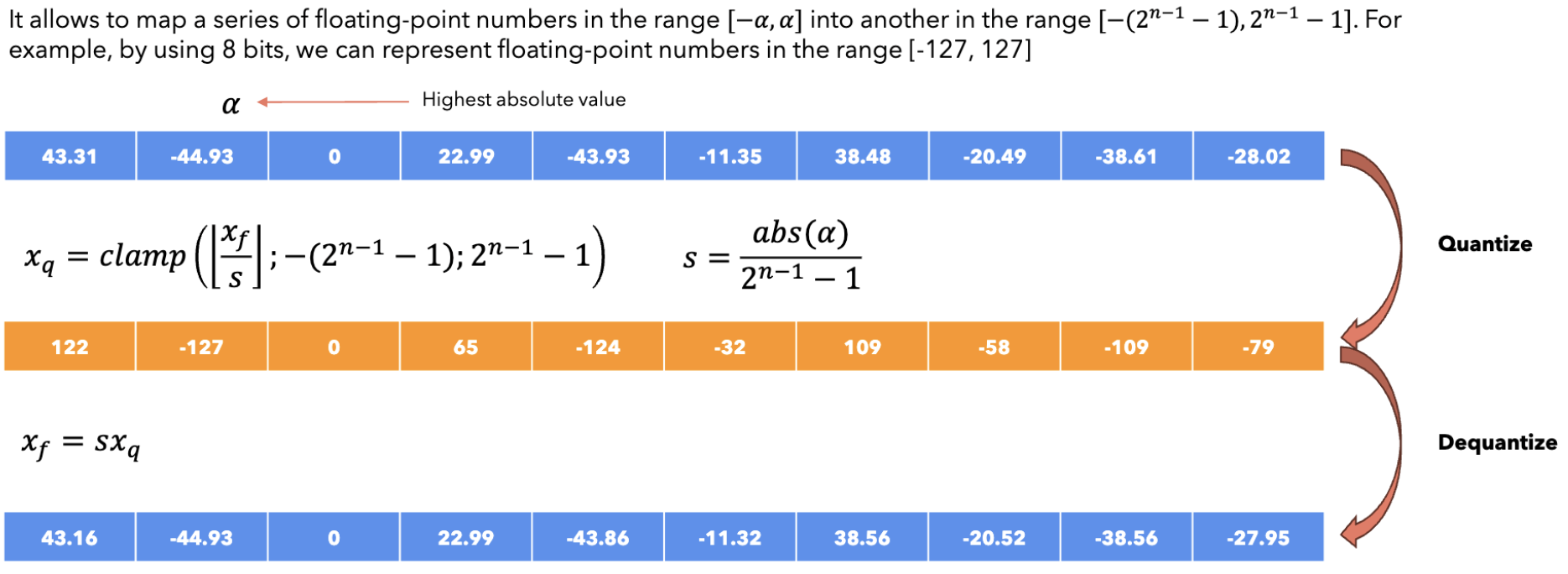
Symmetric Quantization¶
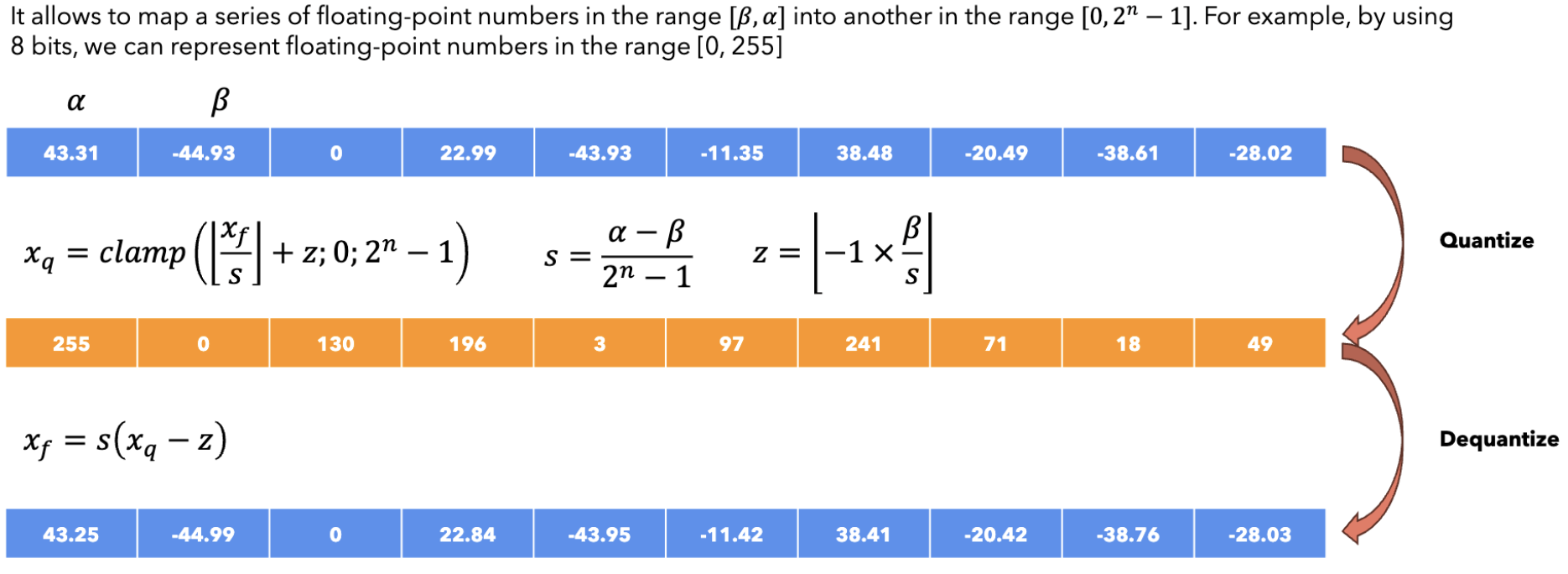
Asymmetric Quantization¶
GPU acceleration¶
When computing $X*W+B$ each row of $X$ is multiplied by each column of $W$ and then added to $B$. The GPU can perform this computation in parallel for each row of $X$ and each column of $W$ by using Multiply-Accumulate (MAC) operations.
How to choose the range of the quantization?¶
- Use the minimum and maximum value of the weights and activations
- Use the mean-square error (MSE) of the weights and activations
- Cross-entropy
Code¶
Create a simple tensor with random items¶
In [1]:
import numpy as np
# Suppress scientific notation
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
# Generate randomly distributed parameters
params = np.random.uniform(low=-50, high=150, size=20)
# Make sure important values are at the beginning for better debugging
params[0] = params.max() + 1
params[1] = params.min() - 1
params[2] = 0
# Round each number to the second decimal place
params = np.round(params, 2)
# Print the parameters
print(params)
[135.27 -40.19 0. 71.58 0.15 89.11 -39.19 -12.81 -14.72 128.6 -28.3 113.96 134.27 -25.94 36.49 53.55 24.1 133. 32.29 97.02]
Define the quantization methods and quantize¶
In [2]:
def clamp(params_q: np.array, lower_bound: int, upper_bound: int) -> np.array:
params_q[params_q < lower_bound] = lower_bound
params_q[params_q > upper_bound] = upper_bound
return params_q
def asymmetric_quantization(params: np.array, bits: int) -> tuple[np.array, float, int]:
# Calculate the scale and zero point
alpha = np.max(params)
beta = np.min(params)
scale = (alpha - beta) / (2**bits-1)
zero = -1*np.round(beta / scale)
lower_bound, upper_bound = 0, 2**bits-1
# Quantize the parameters
quantized = clamp(np.round(params / scale + zero), lower_bound, upper_bound).astype(np.int32)
return quantized, scale, zero
def asymmetric_dequantize(params_q: np.array, scale: float, zero: int) -> np.array:
return (params_q - zero) * scale
def symmetric_dequantize(params_q: np.array, scale: float) -> np.array:
return params_q * scale
def symmetric_quantization(params: np.array, bits: int) -> tuple[np.array, float]:
# Calculate the scale
alpha = np.max(np.abs(params))
scale = alpha / (2**(bits-1)-1)
lower_bound = -2**(bits-1)
upper_bound = 2**(bits-1)-1
# Quantize the parameters
quantized = clamp(np.round(params / scale), lower_bound, upper_bound).astype(np.int32)
return quantized, scale
def quantization_error(params: np.array, params_q: np.array):
# calculate the MSE
return np.mean((params - params_q)**2)
(asymmetric_q, asymmetric_scale, asymmetric_zero) = asymmetric_quantization(params, 8)
(symmetric_q, symmetric_scale) = symmetric_quantization(params, 8)
print(f'Original:')
print(np.round(params, 2))
print('')
print(f'Asymmetric scale: {asymmetric_scale}, zero: {asymmetric_zero}')
print(asymmetric_q)
print('')
print(f'Symmetric scale: {symmetric_scale}')
print(symmetric_q)
Original: [135.27 -40.19 0. 71.58 0.15 89.11 -39.19 -12.81 -14.72 128.6 -28.3 113.96 134.27 -25.94 36.49 53.55 24.1 133. 32.29 97.02] Asymmetric scale: 0.6880784313725491, zero: 58.0 [255 0 58 162 58 188 1 39 37 245 17 224 253 20 111 136 93 251 105 199] Symmetric scale: 1.0651181102362206 [127 -38 0 67 0 84 -37 -12 -14 121 -27 107 126 -24 34 50 23 125 30 91]
Dequantize the parameters back to 32 bits¶
In [3]:
params_deq_asymmetric = asymmetric_dequantize(asymmetric_q, asymmetric_scale, asymmetric_zero)
params_deq_symmetric = symmetric_dequantize(symmetric_q, symmetric_scale)
print(f'Original:')
print(np.round(params, 2))
print('')
print(f'Dequantize Asymmetric:')
print(np.round(params_deq_asymmetric,2))
print('')
print(f'Dequantize Symmetric:')
print(np.round(params_deq_symmetric, 2))
Original: [135.27 -40.19 0. 71.58 0.15 89.11 -39.19 -12.81 -14.72 128.6 -28.3 113.96 134.27 -25.94 36.49 53.55 24.1 133. 32.29 97.02] Dequantize Asymmetric: [135.55 -39.91 0. 71.56 0. 89.45 -39.22 -13.07 -14.45 128.67 -28.21 114.22 134.18 -26.15 36.47 53.67 24.08 132.8 32.34 97.02] Dequantize Symmetric: [135.27 -40.47 0. 71.36 0. 89.47 -39.41 -12.78 -14.91 128.88 -28.76 113.97 134.2 -25.56 36.21 53.26 24.5 133.14 31.95 96.93]
Calculate the quantization error¶
In [4]:
print(f'{"Asymmetric error: ":>20}{np.round(quantization_error(params, params_deq_asymmetric), 2)}')
print(f'{"Symmetric error: ":>20}{np.round(quantization_error(params, params_deq_symmetric), 2)}')
Asymmetric error: 0.03 Symmetric error: 0.06
In [ ]: